2016-08-04
Civil and structural Engineering
- Client: Center Balexert SA
- Assignment: Full civil engineering specialist services
- Total cost of work: 70,000k CHF (complete work)
- Total cost of the assignment: 680 kCHF
- Completion date: 2018-2010
PROJECT DESCRIPTION AND CHARACTERISTICS
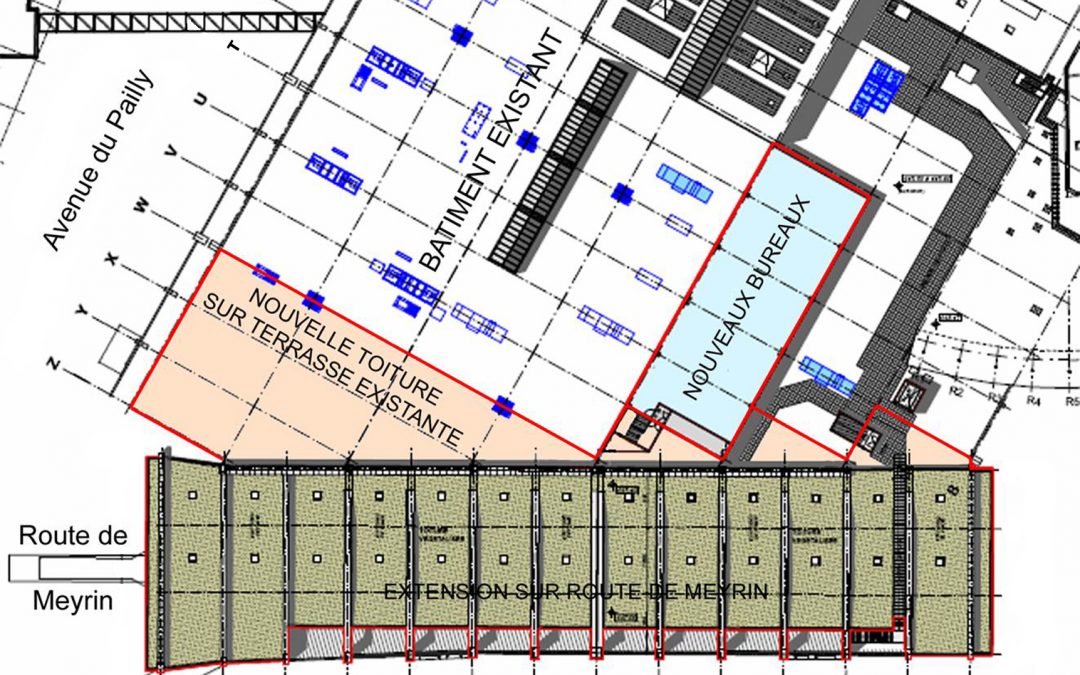
First major shopping center in French-speaking Switzerland, the Balexert Shopping Center was inaugurated in 1971 and converted for the first time during the years 1990 to 2000. The whole complex offers a surface of 134,700 m², on two semi-subterranean levels of parking lot and two floors above the ground floor.
The project of westward extension, spans over the Meyrin road and offers 7,600 m² of additional commercial area on two levels and 840m² of offices on the roof level. The structural report of the extension was executed by the design offices T ingénierie & ZS ingénieurs civils.
Conversion and connection to the existing building were carried out step by step, with the shops remaining in service. The solution of a steel-concrete composite structure with a 17m span was chosen to create the new slabs. The creation of the roof level offices required demolition of the existing roof in order to recreate a floor about 1m above the existing level and thus increase the ceiling height.
ASSIGNMENT
Holder of the mandate for the structural aspects of the conversion and connection to the existing structure. The services were carried out in the legal company name of Sansonnens SA, which joined GEOS in 2014.
Realization of the complete services under the SIA 103 regulation (Swiss Standard), ie: project studies, tender and implementation (project execution and follow-up).

2016-08-04
Civil and structural Engineering
- Client: Municipality of Yverdon-les-Bains – Department of Works and Environment
- Assignment: Complete Project Management
- Total cost of work: 21,500 kCHF (December 2016)
- Total cost of the assignment: 600 kCHF
- Completion date: 2014-2019
PROJECT DESCRIPTION AND CHARACTERISTICS
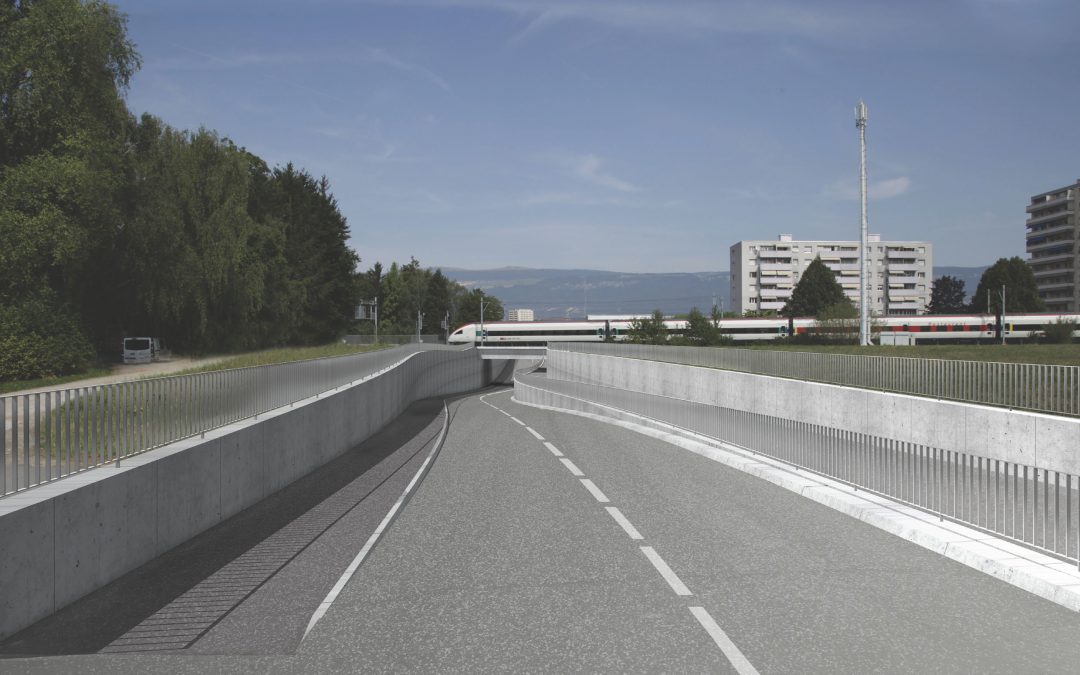
The project consists of designing and constructing a bypass road southwest of the city of Yverdon-les-Bains, aimed at relieving the Yverdon-South junction of the N1 and limiting traffic to the city center.
An access hopper and an underpass with a length of 220m are required for the crossing of the double-track Lausanne-Yverdon railway line.
The characteristics of the project are as follows:
- Length of the new road about 1 km
- Mobility track of 3.5 m in own site
- Bike rack of 1.65 m
- Width of road 6.70 m
- Construction of a canal (valley) for the evacuation of surface water run-off
- Hopper and underpass length 220 m
- Clearance gauge in the underpass of 5.80 m (height for exceptional convoys)
- Width of hopper and underpass 14.50 m
- Depth of underpass 8.5 m below the natural ground
- Pumping of surface water run-off in the hopper to the evacuation valley
- Installation of 2 provisional 24 m long steel railway bridges supported on second jet grouted columns (diameter 300mm) for the maintenance of rail traffic throughout the duration of the works
- Main constraints: poor bearing capacity of the subsoil and a very high groundwater level (70 to 30 cm below the natural ground).
- 6000 m² of 1m thick slurry walls (permanent supports in access hoppers)
- 540 m² of sheet piling (provisional supports for groundworks under the railway)
- 5000 m³ of concrete, 800 tons of reinforcement
- 20,000 m³ of groundworks for the construction of the crossing structure (hoppers + underpass structures)
- drain wells for lowering of phreatic groundwater table Inside waterproof site
- Installation of drainage systems 700 ml
ASSIGNMENT
GEOS is in charge of the project management task as a coordinating contractor for the “Pool GESY” (joint contracting of GEOS and Synaxis SA-Lausanne)
These studies consist in particular of performing the following services (according to SIA 103 (Swiss Standard)):
- Phase 31: Preliminary project;
- Phase 32: Construction project;
- Phase 33: Permit obtaining, procedure/submitted project;
- Phase 41: Invitations to bid, comparisons of proposals, application for contract awarding;
- Phase 51: Construction Project;
- Phase 52: Implementation;
- Phase 53: Commissioning and completion.
In addition to the basic services, GEOS also conducted the stability analysis of groundworks under the railway and the settlement analysis of provisional railway bridge supports by 3D finite elements modeling on Zsoil software.

2016-08-04
Environnemental Engineering (Fish pass structures)
- Client: VOEnergies Production SA
- Assignment: Complete Project Management
- Total cost of work: 400 kCHF
- Total cost of the assignment: 48 kCHF
- Completion date: 2009-2013
PROJECT DESCRIPTION AND CHARACTERISTICS
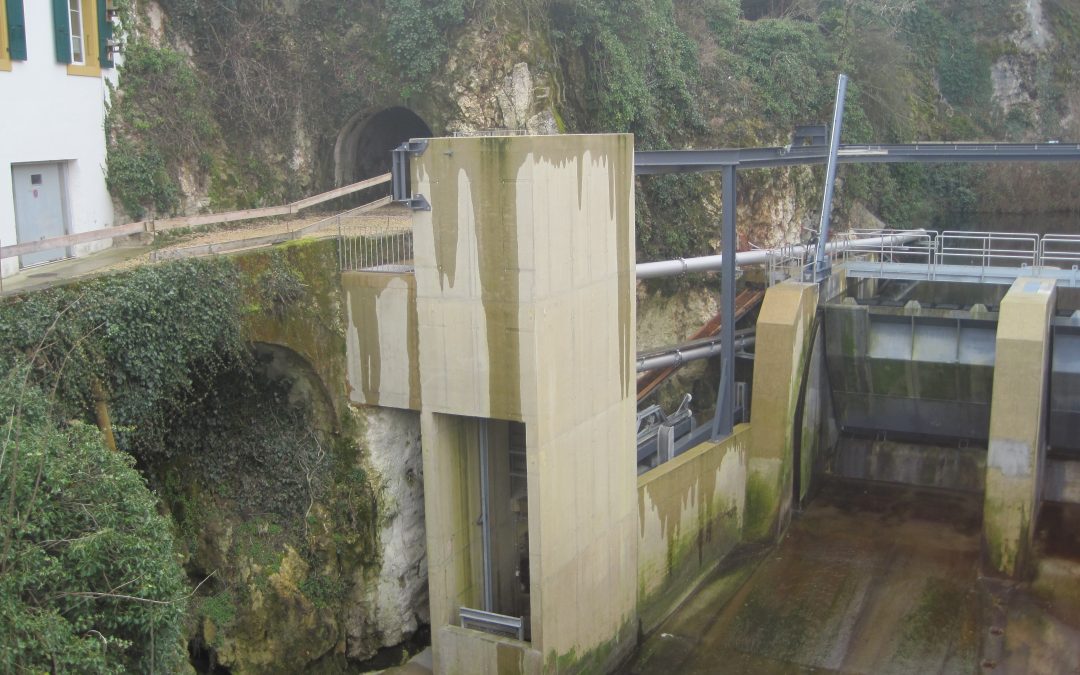
As part of the construction of the Moulinets dam, GEOS studied a concept of crossing the fall of nearly 7m to ensure the free migration of fish.
Given the difficulties encountered in installing a conventional poolway, the installation of a fish lift has proved to be a proven solution in narrow situations where there is a clear lack of space.
The principle of such a structure is relatively simple: by placing the lift in the same place where the fish accumulate at the foot of the dam, the fish are attracted by an attraction flow of 350 l / s, supplied by a DN350 stainless steel pipe from the reservoir to the lift. For the attracting current produced to be sufficient (with a speed of 1.5 m / s), an opening of reduced size is placed at the lift entrance.
The fish are therefore attracted to a net that carries them about 7m higher. From there, they are brought to harbor with the aid of water pumped in a pipe over the crest of the dam.
The climbing and descent movements are automated and according to a periodicity depending on the time of year and the species to be transported.
With regard to downstream migration, a system of removable flaps has been implemented in the control grid of the plant. When the grid flaps are raised, fish can pass through the grid. They are then recovered in a chute, followed by a trapping tank and a downstream discharge pipe.
ASSIGNMENT
These studies consist in particular of performing the following services (according to SIA 103 (Swiss Standard)):
- Phase 31: Pre- Project;
- Phase 32: Design of works;
- Phase 33: Application Procedure;
- Phase 41: Invitations to tender, comparisons of bids, proposals for tenders;
- Phase 51: Implementation Project;
- Phase 52: Execution of works;
- Phase 53: Commissioning, completion

2016-08-04
Environmental Engineering (Renaturation of water courses)
- Client: State of Geneva – Service of Renaturation of Water Courses
- Assignment: Project Management and design
- Total cost of work: 800k CHF
- Total cost of the assignment: 110k CHF
- Completion date: 2012-2014
PROJECT DESCRIPTION AND CHARACTERISTICS
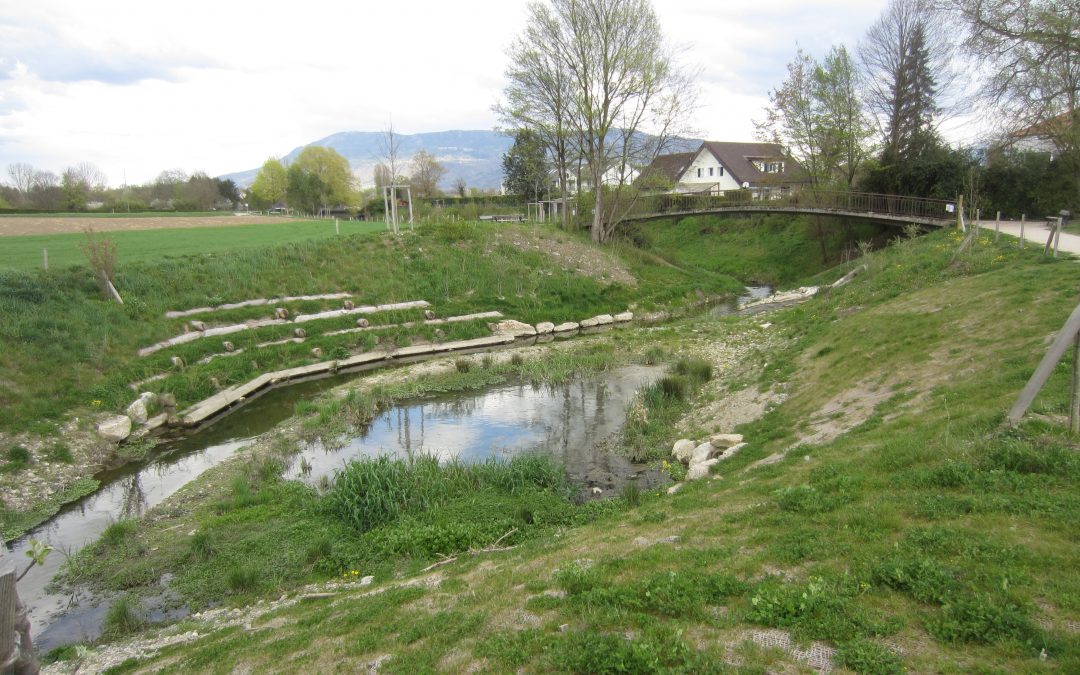
The project consists of restoring the river to a morphology close to its natural state, completely redesigning the banks and the low-flow channel of the watercourse that appeared before as a channel, while making sure to maintain the hydraulic conditions during floods.
The works include:
- Demolition of concrete culvert, creation of meanders to get flow diversity, creation of new wetlands to increase biodiversity and develop biotopes;
- Revegetation of the banks on biodegradable geotextile (coconut mat) – Planting of species corresponding to the plants that are normally encountered in this type of environment in order to accelerate re-greening, to limit risks associated with neophytes and to improve stability of banks and slopes;
- Realization of vegetated wooden caissons with fish shelters;
- Moving the walking path out of the space close to the watercourse in order to respect the function of biological corridor as much as possible;
- Renovation of relaxation and walking areas.
For a 430m renatured reach, about 1,800 m³ of concrete and blocks were removed from the watercourse, for a volume of earthwork of 10,000 m³.
ASSIGNMENT
GEOS has carried out complete management and design of the project, in association with an aquatic environment specialist, including:
- Preliminary study;
- Conceptual design;
- Advanced hydraulic analysis;
- Design of works;
- Procedure for requesting authorization;
- Preparation of the tender documents, bid analysis;
- Detailed design;
- Site supervision.
2016-08-04
Environmental Engineering
- Client: DuPont Polymers Powder Switzerland
- Completion date: 2010
PROJECT DESCRIPTION AND CHARACTERISTICS
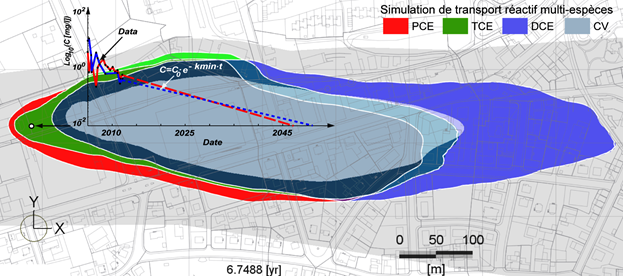
A multi-species reactive transport model was developed to estimate the time required for attenuation of chlorinated solvents that pollute an industrial site.
Two main variants were modeled:
(1) natural attenuation of pollution by biodegradation and
(2) active treatment of the sources of pollution by injection of a stimulating solution
ASSIGNMENT
GEOS was in charge of:
- statistical processing of concentration data,
- validation of a permanent flow pattern in free groundwater,
- calibration of reactive multi-species transport parameters,
- sensitivity analysis on PCE degradation constants, TCE, TCE and CV,
- predictive simulations of evolution of the pollution for various scenarios including active treatment of all pollution source zones by injection of a substrate stimulating bacterial activity, responsible for the degradation of the chlorinated solvents.
- the feasibility study of active treatment.





